Are you grappling with the complexities of remotely accessing your IoT devices, perhaps a Raspberry Pi, that's nestled behind a firewall or a labyrinthine NAT configuration? The good news is, achieving secure remote access to these devices, even without wrestling with port forwarding, is entirely within your grasp.
The modern landscape of the Internet of Things (IoT) presents both incredible opportunities and daunting challenges. As more and more devices become interconnected, the ability to manage and interact with them remotely becomes paramount. This is especially true when those devices are deployed in physically challenging or hazardous environments, or when they are behind network configurations that make direct access difficult or impossible.
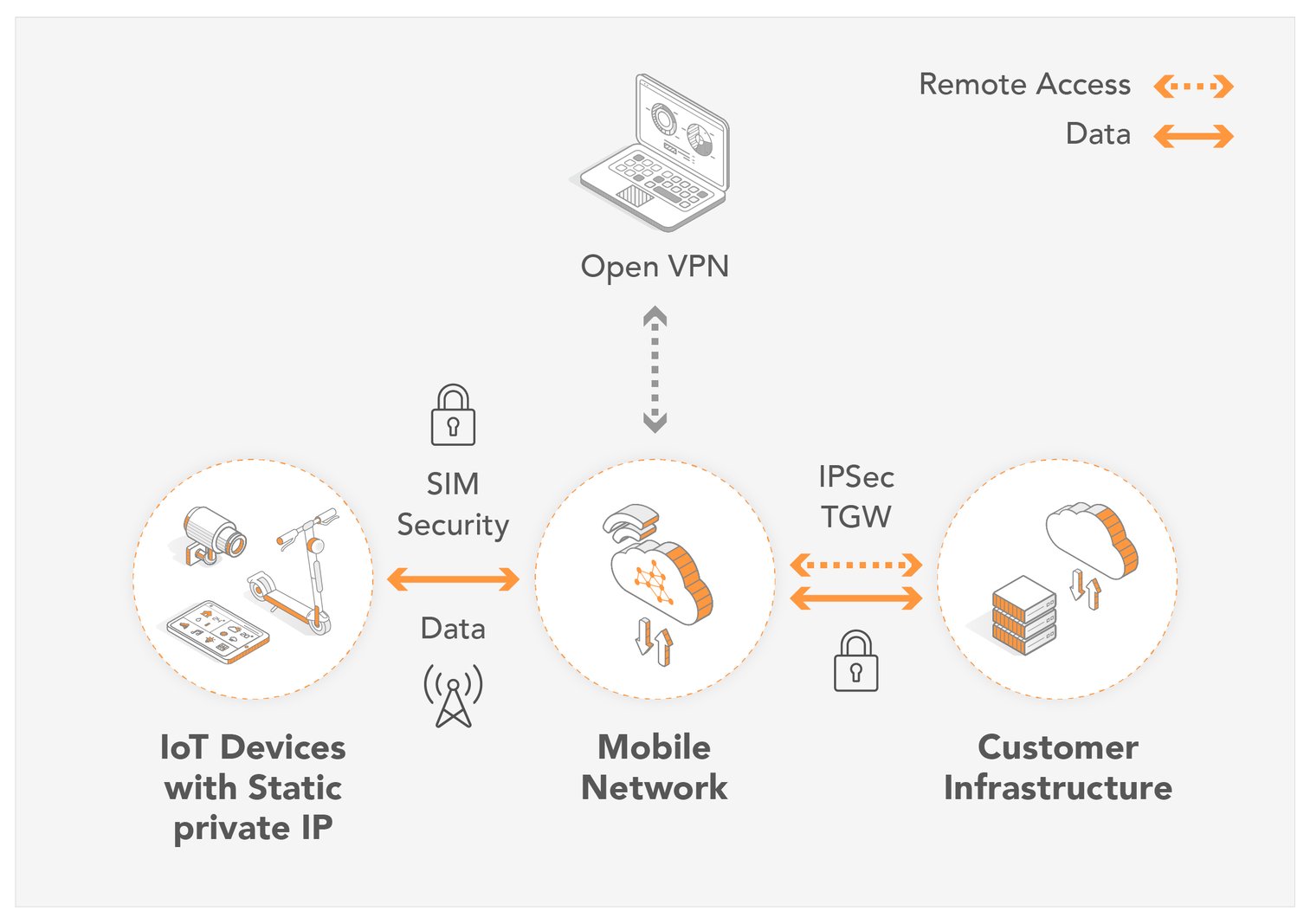
Consider scenarios where IoT devices are deployed in remote locations, such as weather stations in desolate areas, or industrial equipment in inaccessible parts of a factory. Remote access is not just a convenience; it's a necessity for monitoring, maintenance, and troubleshooting. This is where the concept of secure remote access solutions becomes critical, allowing for efficient and safe management of these devices from anywhere in the world.
The inherent challenge, however, lies in the network configurations often encountered in real-world deployments. Devices behind Network Address Translation (NAT) firewalls or those behind Carrier-Grade NAT (CGNAT) often lack a public IP address, making direct access through conventional methods, such as SSH (Secure Shell) with port forwarding, problematic. This is where alternative methods and solutions become crucial.
The common method of SSH, which by default utilizes TCP port 22, is a well-established method for secure communication. It offers a robust cryptographic network protocol to establish a secure channel between two systems. However, it requires that the server is reachable, and the client knows the servers IP address. This is where the complexities of NAT and firewalls come into play. For many, managing port forwarding becomes an exercise in IT administration, with potential security implications if not configured correctly.
So, how do we bypass these hurdles? Let's delve into a practical approach. Several innovative solutions are available. For example, tools such as Pinggy provide elegant methods for temporary SSH access. The essential principle is creating an intermediary, a bridge if you will, through which your device can be accessed. A slightly different approach uses tools such as SocketXP, which simplifies the process of establishing a secure tunnel for remote access.
Before we move to the mechanics, its worth reminding ourselves of the fundamentals: an SSH server needs to be running on the target machine, whether that's a Raspberry Pi or any other IoT device. This server listens for incoming connections, authenticates the user, and then grants access. The specific setup varies based on the operating system and device, but the core principle remains the same: establish a secure connection and open a pathway to the device.
Let's imagine you have your Ubuntu machine up and running, with an SSH server installed. The basic syntax to connect is as follows: In your Mac terminal, you'd type something like: ssh {your ubuntu user}@{your ubuntu ip}. You'll be prompted for your Ubuntu user's password. If you can successfully authenticate, and assuming the basic network path is clear, you will then be able to access the Ubuntu prompt, and thus, control the server.
Now, consider the more complex scenario, where a direct connection is impossible. Here, you turn to methods that circumvent port forwarding. Tools like SocketXP and others offer solutions that create a secure tunnel, eliminating the need to manage complex network configurations.
Let's focus on the method employing SocketXP, and explain how to use it for your project. The first step involves installing the SocketXP Linux server remote access agent. This agent will run on both the IoT device (e.g., Raspberry Pi) and the machine from which you intend to access it. By establishing a secure connection through their service, they bypass the need for port forwarding.
Several vendors provide solutions to streamline the remote access process. Macchina.io remote offers secure remote access via web, shell (ssh), file transfer (ssh, sftp), and remote desktop (vnc, rdp). It is also possible to maximize remote workforce productivity by providing users with fast, secure access to Windows, Mac, & Linux desktops located anywhere in the world. You can also use Xrdp which also makes remote access to your IoT simple.
Remote access tools offer various protocols to connect. VNC (Virtual Network Computing) and RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol) are two protocols. VNC, particularly, is also known as the Remote Frame Buffer (RFB) protocol, and is an option for remote desktop access. On Ubuntu, the "vino" VNC server can be configured through the Ubuntu Gnome desktop environment, specifically under System > Preferences > Remote Desktop.
To summarize the steps, begin by updating and upgrading your Ubuntu server. Consider selecting and installing a desktop environment, such as Gnome, KDE Plasma, or XFCE, depending on your preferences and the device's resources. Next, make sure you have an SSH client installed on the machine you are using to initiate the remote connection. Install the SocketXP agent on your IoT device by downloading it from their official site. Follow the agent-specific configuration instructions to establish the secure tunnel and finally connect.
Consider that remote IoT device management is particularly useful when your IoT devices are deployed in physically dangerous or challenging-to-reach environments. You need to get status updates about the health and condition of the device. Remote access is, therefore, a crucial element of reliable IoT device management.
Understanding and implementing secure remote access to your IoT devices are essential steps in unlocking their full potential. By embracing these techniques, you can confidently manage your devices regardless of their location or the intricacies of their network setup.
For deeper understanding, resources such as "How to remote access IoT web app over the internet" are available. Also, tools that let you "Send remote commands to IoT over the internet from outside network" are readily accessible.
So, if you are faced with the need to securely access your Ubuntu desktop, server, or cloud resources without knowing where to start, you have the resources at your disposal. As organizations continue to embrace remote work, secure remote access to Linux environments becomes increasingly critical. This is why we have identified the essential steps to set up a solution, specifically using the SocketXP IoT agent for remote SSH access to your IoT devices. By following these steps, you will be well on your way to securely managing your devices, no matter where they are located.
Remember to first download and install the SocketXP IoT agent on your IoT device from the provided link.